SQL JOINs
SQL JOINs are a way of combining records from two or more tables in a database.
A JOIN is a means of combining fields from two tables using values that are common to both.
Types of JOINs
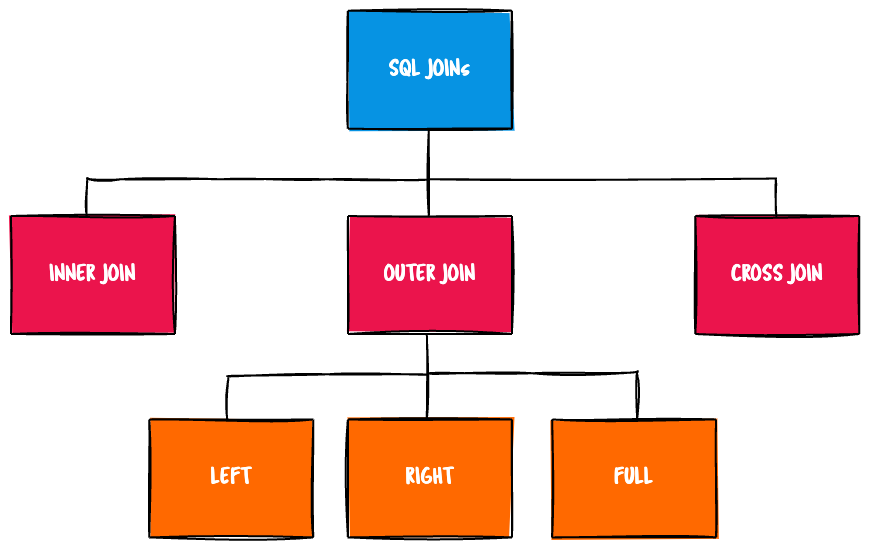
SQL defines three major types of JOINs.
INNER JOIN
An INNER JOIN is the most common type of JOIN and is the default type of JOIN. Using the INNER keyword is optional. This JOIN selects all rows from both participating tables as long as there is a match between the columns.
OUTER JOIN
OUTER JOINs can be sub-classified into LEFT, RIGHT, and FULL OUTER JOINs. Using the OUTER keyword is optional. This returns all rows from both the participating tables that satisfy the JOIN condition, along with rows that do not satisfy the JOIN condition.
CROSS JOIN
In a CROSS JOIN, each row from
table1is matched with each row fromtable2, creating a Cartesian product.
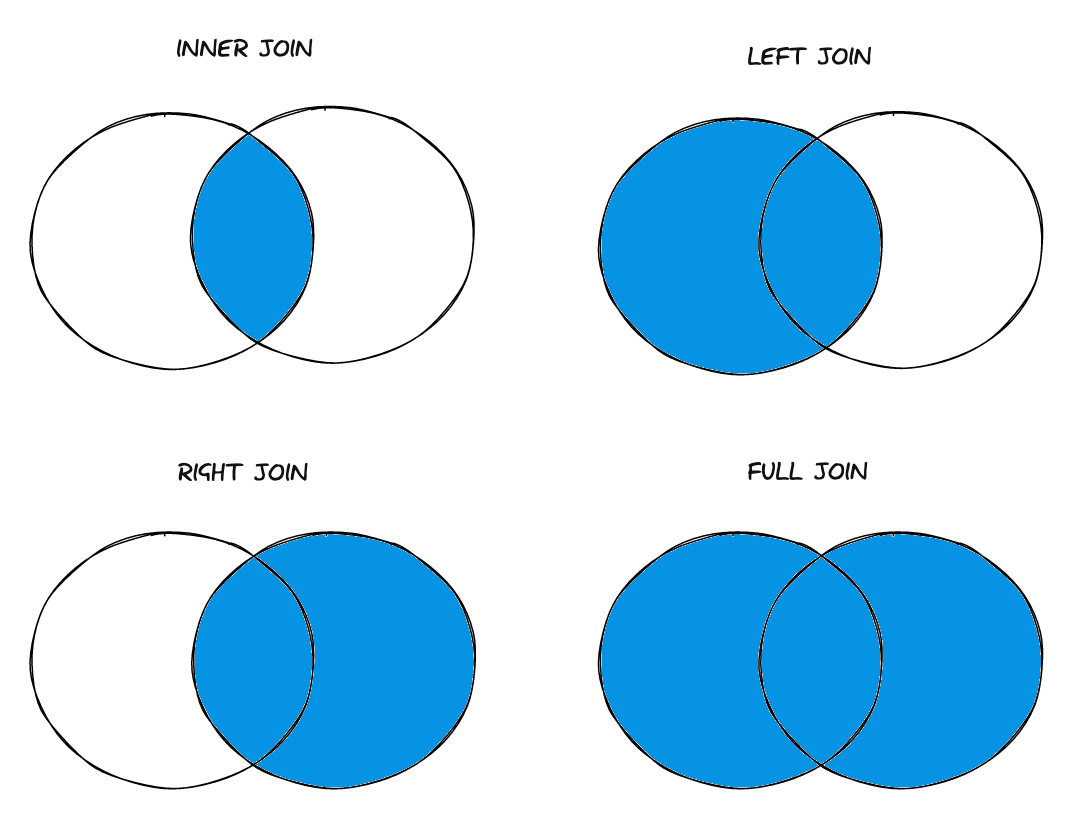
A common (but disputed) way of visualising JOINs is with Venn diagrams:
Colours Database
Let's try out the JOINs with simple data to help visualise how they work.
[INNER] JOIN
An INNER JOIN will return all matching rows in BOTH tables.

LEFT [OUTER] JOIN
A LEFT JOIN will return all rows from the left table with the matching rows from the right table. If there is no match, the right side will be set to null.

RIGHT [OUTER] JOIN
A RIGHT JOIN is just a reverse LEFT JOIN.
FULL [OUTER] JOIN
A FULL JOIN will return all matched and unmatched rows from both tables, setting null on either side if there's no match.

CROSS JOIN
A CROSS JOIN will return every combination of rows from both tables.

[INNER] JOIN
Let's consider two tables, EMPLOYEES and DEPARTMENTS:
EMPLOYEES:
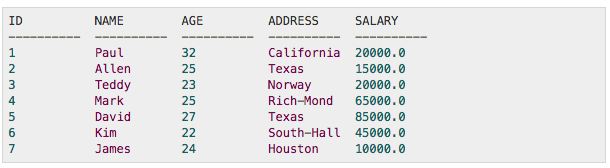
The table has five columns: ID, NAME, AGE, ADDRESS, and SALARY.
DEPARTMENTS:

The table has three columns: ID, DEPT, and EMP_ID.
Based on the tables above, we can write an INNER JOIN as follows:
The query will produce the following result:

As we can see from the query, we compare the tables based on one column in each:
IDin theEMPLOYEEStable.EMP_IDin theDEPARTMENTStable.
The returned data includes information about EMP_ID, NAME, and DEPT.
Further Reading
Last updated